5G CrowdCell啟動你的5G體驗
5G CrowdCell is a fully fledged, open RAN small cell network-in-a-box solution. It uses existing macro 4G networks as backhaul and can be utilized for network-as-a-service (NaaS) deployment, delivering an app-enabled path covering any standard from IoT to 5G
Email Sales
Introduction
The 5G era is upon us. This next generation of mobile communication technology — featuring high bandwidth, low latency and massive connectivity — enables IoT at scale and will revolutionize the way that both people and smart devices communicate.
GIGABYTE and Lime Micro's LimeNET CrowdCell provides the most flexible and future-proof solution for 5G communication. It is low cost, low power consumption, small form factor and deployed with unprecedented ease, to extend coverage and increase capacity of indoor and remote networks alike, while utilizing three key features of 5G to deliver a step change in user experience.
User Scenario
VR 360 video streaming
The increasing demands placed by ever more advanced multimedia content requires high transmission capacity at high transmission speed. 5G feature, eMBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband), supports 8K 360 video streaming and AR/VR performance to significantly enhance the end user experience.

Smart Transportation
Smart vehicles can now see and think for themselves, but to fully realise their potential will require a paradigm shift in connectivity. 5G CrowdCell can be used as a RAN/gateway for connecting/managing all the wireless devices in the vehicle and communicate the information to outside via the nearest macro to improve both functionality and safety.

Smart Cities
5G mMTC (Massive Machine Type Communications) will enable true global scale IoT. Applications include smart buildings and energy grids, real-time enterprise, ubiquitous industrial and consumer IoT, and eHealth. With the potential to deliver new levels of business and eco efficiency, together with increased quality of life for citizens.

Healthcare
CrowdCell with associated sensors and cameras can detect, track and notify the operators and users of the health status of people entering healthcare environment, or transmit patient's health condition in real-time manner in order to have nursing staff's response to take actions.

Challenges of Implementing 5G
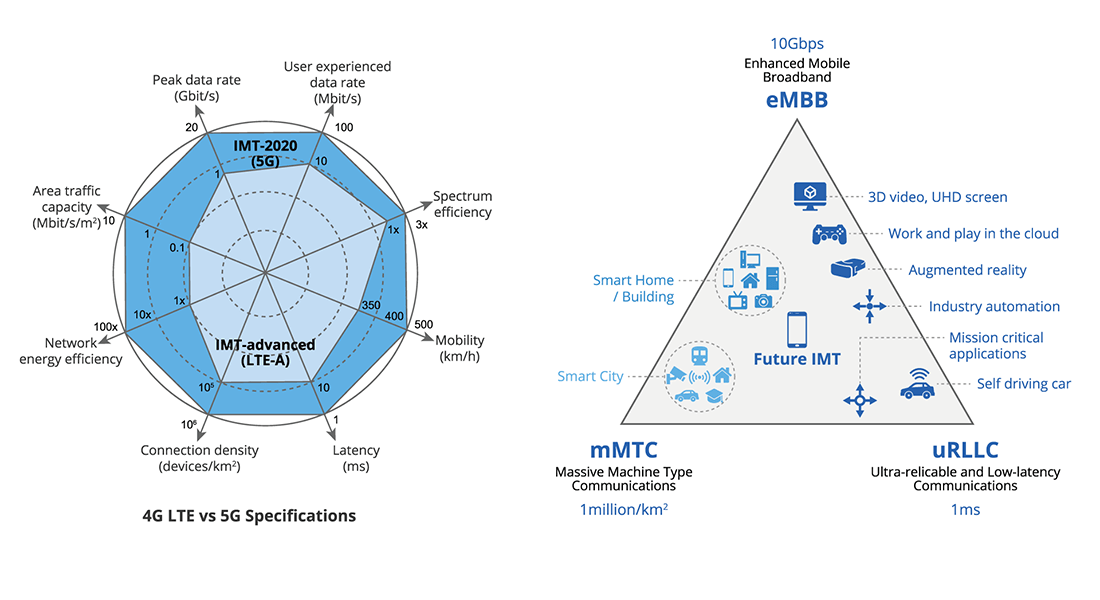
5G - the next generation of mobile telecommunications technology, is on the horizon and promises to deliver a myriad of new services and capabilities such as Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), Ultra Reliable Low-Latency Communications (URLLC) and Massive Machine-Type Communications (mMTC). A new band of the radio frequency spectrum between 30 – 300GHz has been opened for use, and a new telecommunications standard for 5G has been defined encompassing network speed, latency, the number of devices that can be connected, QoS and other conditions.
However, 5G signals use higher frequency radio waves, meaning that the signal strength will decrease further with distance and the transmission range is more limited. Traditional base stations are costly and difficult to deploy, due to scarce land resources and planning complexities. Therefore, 5G small cells will become the optimal solution for network communication.
However, 5G signals use higher frequency radio waves, meaning that the signal strength will decrease further with distance and the transmission range is more limited. Traditional base stations are costly and difficult to deploy, due to scarce land resources and planning complexities. Therefore, 5G small cells will become the optimal solution for network communication.
4G LTE vs. 5G and Usage Scenarios
Features of GIGABYTE & Lime Micro's 5G CrowdCell
Extendable Network Topology
・CrowdCell can be used to extend the current coverage, dynamically distribute and increase network capacity through data caching.
・Architecturally, CrowdCell is an eNB that is backhauled through the macro BTS network.
・To the end users, the CrowdCell looks like an eNB, but to the macro network, it looks like a UE using a SIM to identify itself to the network.

Extendable Network Topology
Network Throughput Enhancement
・ CrowdCell extends coverage improving customer experience, offering high throughput
・ CrowdCell improves ease of use and reduces OPEX. It requires no cables, no rentals with very low energy bills
・ CrowdCell improves ease of use and reduces OPEX. It requires no cables, no rentals with very low energy bills

Network Throughput Enhancement
Enables Network as a Service Platform

Enables Network as a Service Platform
Enables Numerous Applications
・It enables a significant number of applications, covering a diverse set of use cases.
・It is the only platform backed by numerous developer communities who can provide dedicated applications.
・It is the only platform backed by numerous developer communities who can provide dedicated applications.

GIGABYTE/LimeNET 5G CrowdCell Product Introduction
GIGABYTE/LimeNET 5G CrowdCell is a true software-defined radio (SDR) and the next step in the evolution of the small cell network-in-a-box. It can be used for a virtually unlimited number of wireless and radio access network (RAN) applications, with an open architecture that facilitates rapid application development and which greatly simplifies network integration.
Complete with an integrated SDR card and a dedicated RF front-end module that covers the majority of cellular bands, CrowdCell uses existing macro 4G networks as backhaul and can be utilized for any network-as-a-service deployment. GIGABYTE/LimeNET 5G CrowdCell can provide extended coverage and/or increase the capacity of existing networks, together with accelerating the deployment of highly cost-optimized new network infrastructure developments.
1/1

GIGABYTE/LimeNET 5G CrowdCell
Related Technologies
5G is short for "5th Generation", the name for the next generation of mobile cellular networks. 1G networks brought us the first cell phones, 2G networks allowed for text messaging, and 3G networks introduced mobile internet for the first time. Currently in use is 4G which has been deployed globally since 2009. 4G LTE (Long Term Evolution) is the latest version of 4G that allows a download rate of up to around 200Mbps. However, 4G networks have just about reached the limit of their capabilities at a time when users want even more data and faster speeds for their cell phones and other devices. Therefore, the need for a new type of network technology that can provide faster speeds and transmit more data to more users is pressing.
Technically speaking, "5G" is defined only as a set of standards – such as latency, network connection density, and data transfer rate – that the next generation of mobile networks should be able to achieve. Once these standards can be met, 5G should be able to handle up to 1000 times more traffic than today's networks, and be up to 10 times faster than 4G LTE.
To be able to meet these standards, various new technologies will be needed. For example, to support a huge increase in the number of online devices, a new band on the radio frequency spectrum (between 30 – 300GHz) will be opened for use. However, this band of radio frequency consists of "millimeter waves" which are more easily blocked by buildings and absorbed by plants and rain. Therefore, thousands of small base stations ("small cell technology") will be needed to be installed, forming a relay team to transmit signals around obstacles. In addition, to support the latency requirements of 5G, Multi-access Edge Computing technology (MEC) will need to be introduced on a large scale into cellular networks so that the data that the user needs (such as a streaming video) can exist physically closer to the user.
What is Multi-access Edge Computing (Mobile Edge Computing)? Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC), also known as Mobile Edge Computing, is a network architecture that enables cloud computing capabilities and an IT service environment at the edge of a cellular network. MEC technology is designed to be implemented at cellular base stations or other edge nodes, and enables flexible and rapid deployment of new applications and services for customers. MEC is ideal to be used for the next generation of 5G cellular networks.
What is edge computing? Edge computing is a type of computing network architecture, where computation is moved as close to the source of data as possible, in order to reduce latency and bandwidth use. The aim is to reduce the amount of computing required to be performed in a centralized, remote location (i.e. the "cloud") far away from the source of the data or the user who requires the result of the computation, thus minimizing the amount of long-distance communication that has to happen between a client and server. Rapid advances in technology allowing for miniaturization and increased density of computing hardware as well as software virtualization have made edge computing more feasible in recent years.Learn More:《What is Edge Computing? Definition and Cases Explained.》
加速實現你的科技創新
業務洽詢