- Dual Thunderbolt™ 2 Ports
- 20 Gb/s Bi-directional Bandwidth
- DisplayPort 1.2 Capable with 4K Video Throughout
- Daisy-chain up to 12 Devices (6 devices per port)
-
The Fastest Connection to Your PC Just Got Faster!
 The GC-Thunderbolt 2 offers an easy way to upgrade GIGABYTE Thunderbolt™ ready motherboards with the new and faster Thunderbolt™ 2 connectivity without having to upgrade to a whole new system.
The GC-Thunderbolt 2 offers an easy way to upgrade GIGABYTE Thunderbolt™ ready motherboards with the new and faster Thunderbolt™ 2 connectivity without having to upgrade to a whole new system.
GC-Thunderbolt 2 card with dual Thunderbolt™ 2 ports offers:
• Dual Thunderbolt™ 2 Ports
• 20 Gb/s Bi-directional Bandwidth
• DisplayPort 1.2 Capable with 4K Video Throughout
• Daisy-chain up to 12 Devices (6 devices per port)



-
Upgrade Your Motherboard the Easy Way !

Step 1:
Install the Thunderbolt™ add-in card in the PCIE 2.0 x4 slot.
Step 2:
Connect one end of the THB_C header cable to the TB Header on the Thunderbolt™ add-in card.
Step 3:
Connect the other end of the cable to the THB_C header on the motherboard.
Step 4:
Use the included DisplayPort/Mini DisplayPort cable to connect your graphics card to the Thunderbolt™ add-in card.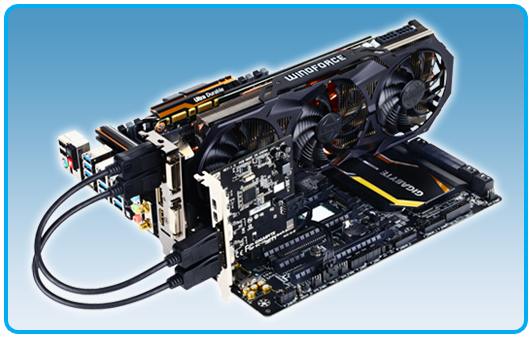
*To enable both two Thunderbolt™ ports, please connect both display port cables to the graphic card. You can find more information about Installation Guide here. -
Compatible Models*
*GC-Thunderbolt 2 Add-in Card is compatible with selected motherboards only. -
Accessories


* I termini HDMI, Interfaccia multimediale ad alta definizione HDMI (HDMI High- Definition Multimedia Interface), immagine commerciale HDMI (HDMI Trade dress) e i loghi HDMI sono marchi commerciali o marchi commerciali registrati di HDMI Licensing Administrator, Inc.
* I materiali qui forniti sono solo di riferimento. GIGABYTE si riserva il diritto di modificare o rivedere il contenuto in qualsiasi momento senza preavviso.
* Le prestazioni pubblicate si basano su valori massimi teorici fornite dai rispettivi fornitori di chipset o organizzazione che hanno definito le specifiche di interfaccia. Le prestazioni effettive possono variare in base alla configurazione del sistema.
* Tutti i marchi ei loghi sono di proprietà dei rispettivi titolari.
* A causa dell'architettura standard del PC, una certa quantità di memoria è riservata al sistema e quindi la capacità di memoria reale è inferiore a quella dichiarata.





















