Introduction
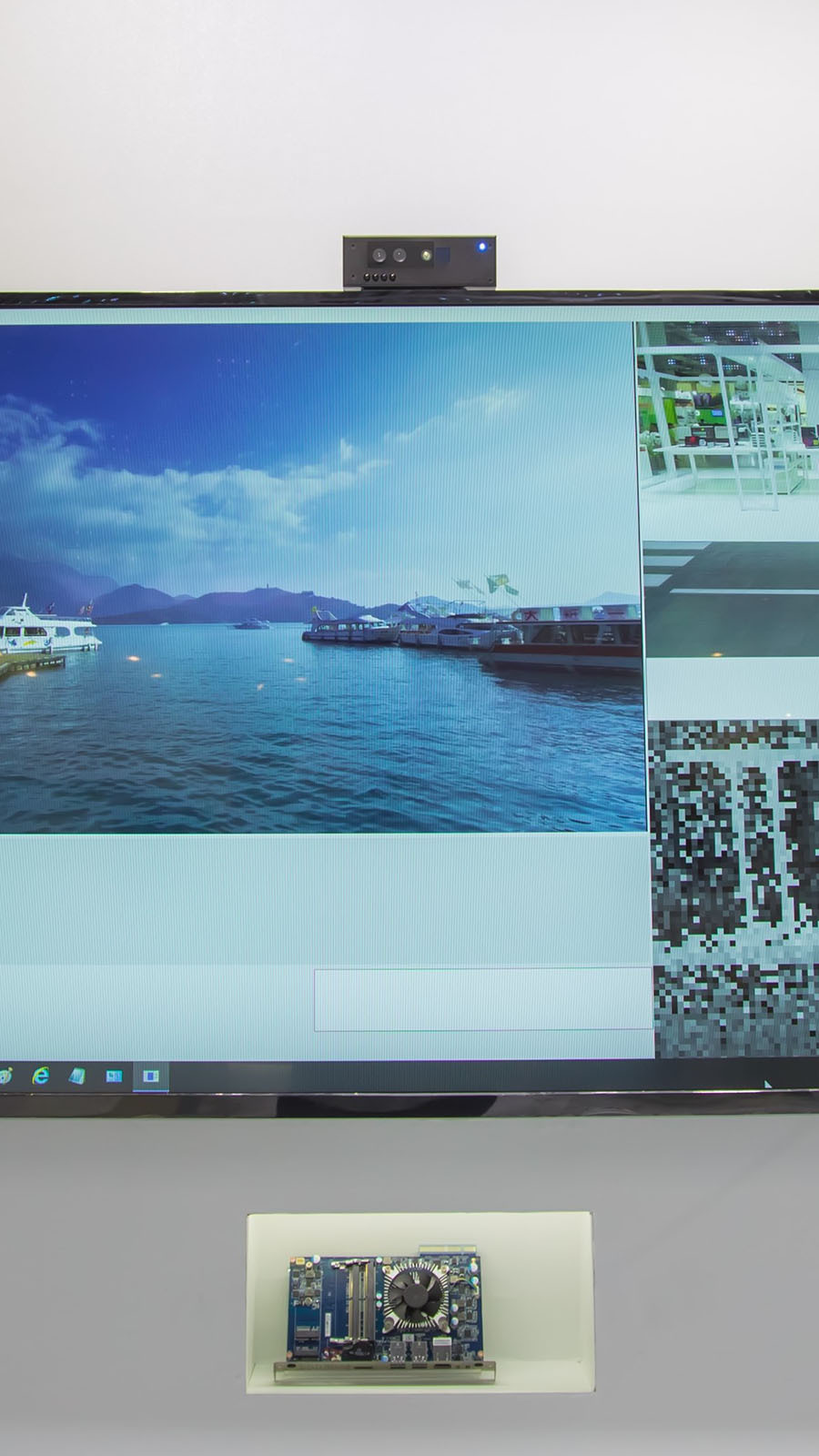
With the growing needs for in-store business, retailers are seeking for digital solutions that brings more immersive interactions with potential customers, providing real-time and targeted advertisements, collecting customer's behaviors and processing data analysis to drive business goals. GIGABYTE and NOEMA 's interactive digital signage is a well-integrated visual display solutions for retail markets to improve customer's experience.
Use Case Scenarios
NOEMA's Software Brings User Experience to New Level
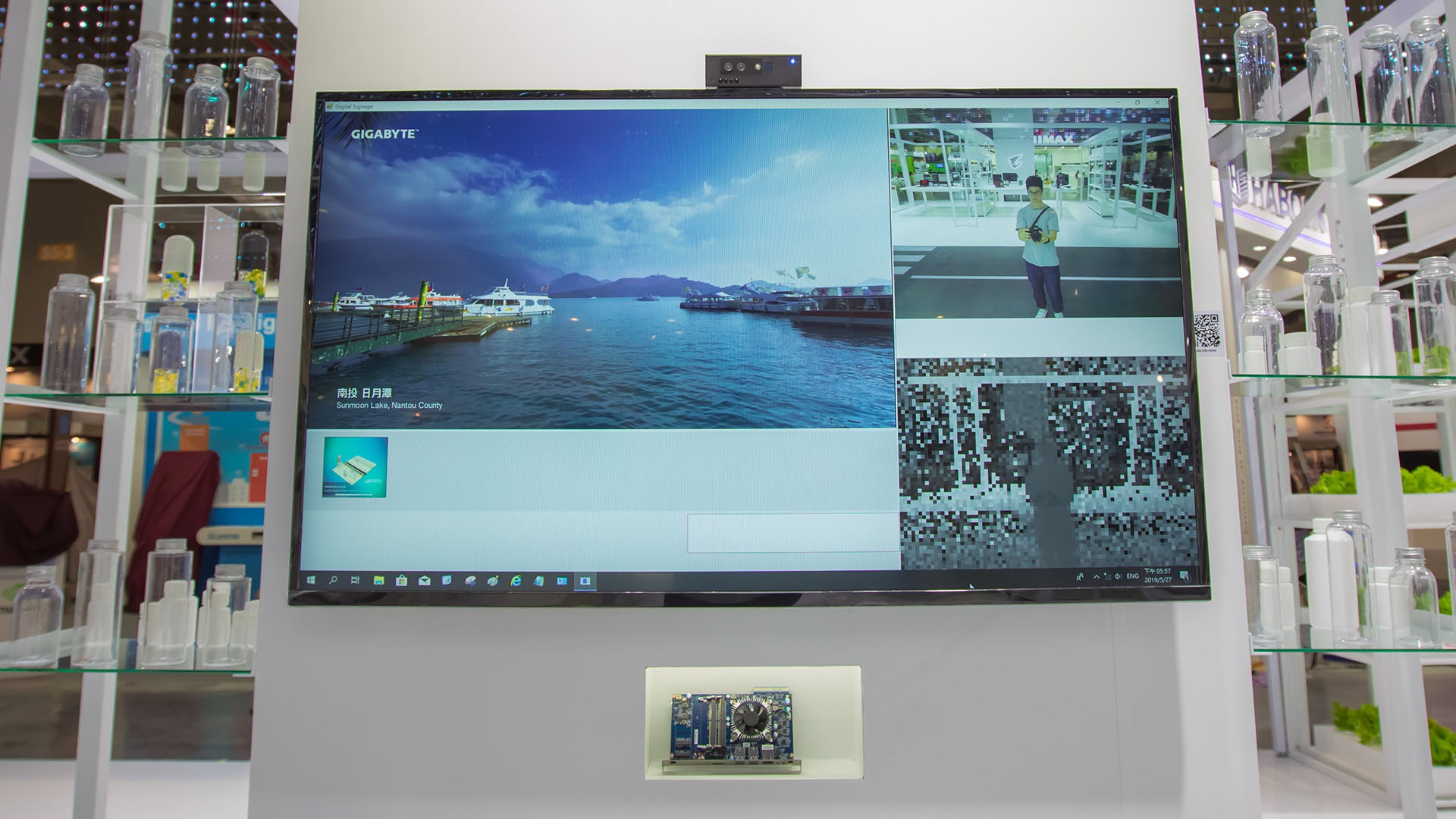
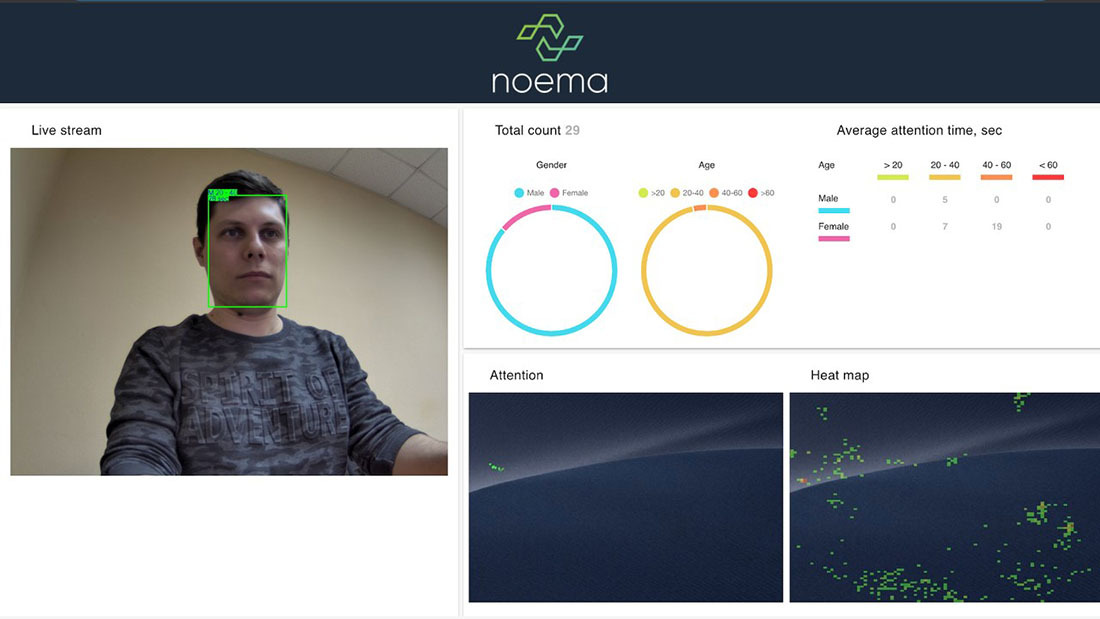
NOEMA's Interactive Digital Signage software solution is the first software product including audience measurement, sight direction tracking and gesture recognition in one package:
・Audience measurement detects age and gender and counts unique customers.
・Sight direction tracking enables touchless video management and heatmap analysis of the displayed content.
・Gesture recognition adds interactivity and user interaction with displayed content.
・All analytics can be done at the edge.
The Benefits of Interactive Digital Signage
Quick Deployment
SDM supports hot swap and is easy to carry & insert in digital signage. Multi-media contents can be pre-installed in the SDM or remotely uploaded.
Real-time Interaction
Interacting with customers by detecting their age and gender to provide target contents to drive further interaction immediately.
Highly Compatibility
Compatible with 3rd party Content Management Systems (CMS)
Data Analysis
Collects statistics and performs analysis on all features: Audience traffic by gender or age, video watch time, etc.
Return on Investment
Stretch your public ads., spend the extra mile by ensuring all users receive targeted content to increase conversion rate.
Highly Integrated Hardware for Interactive Digital Signage
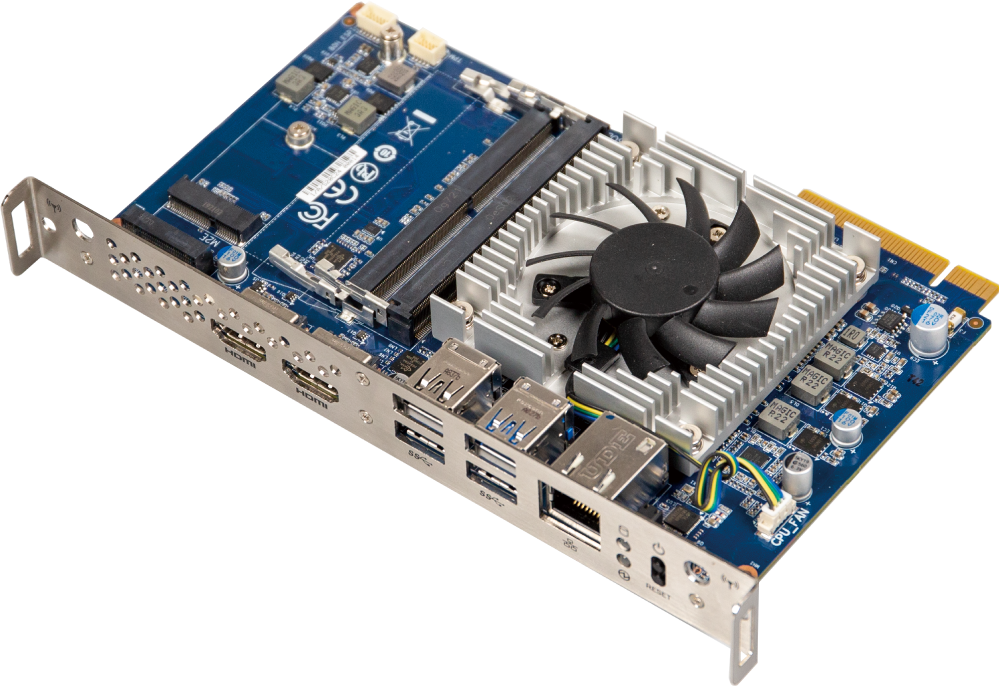
Smart Display Module (SDM) : Compact Size but Powerful Performance
As the display panels in the market keep getting thinner, a slim computing module is a necessity for an all-in-one display solution. Smart Display Module (SDM), a form factor defined by Intel®, is the next generation of display hardware solution that delivers the same level of intelligence and interoperability as the Open Pluggable Specification (OPS), yet the housing is only a 1/3 of the size. GIGAIPC SDM series, supported by Intel® Celeron® N4000 to Core™ i3/i5 processors, is designed for low power consumption, which significantly improves longevity and high computing performance and stability.
With the dimensions of 175mm x 100mm, SDM is designed and built-in a thin client or PC box, but also acts as a standalone module with Windows or Linux operating systems preinstalled for users to "plug-and-play". It is also a convenience for system upgrades and ease of maintenance. It offers multiple I/O interfaces to be connected with various devices based on users' needs, and supports dual independent display outputs of 1 x HDMI and 1 x Display Port. It delivers 4K Ultra HD resolution for eye-catching video content used on multi-screen digital signage. In addition, it incorporates high-speed PCIe connectivity with expansion slots that eliminate the need for external I/O devices.